ARPA Bio
in tune with innovative solutions for early therapeutic intervention...

Novel, early therapeutic approach by targeting the long, insidious phase of Alzheimer's disease.
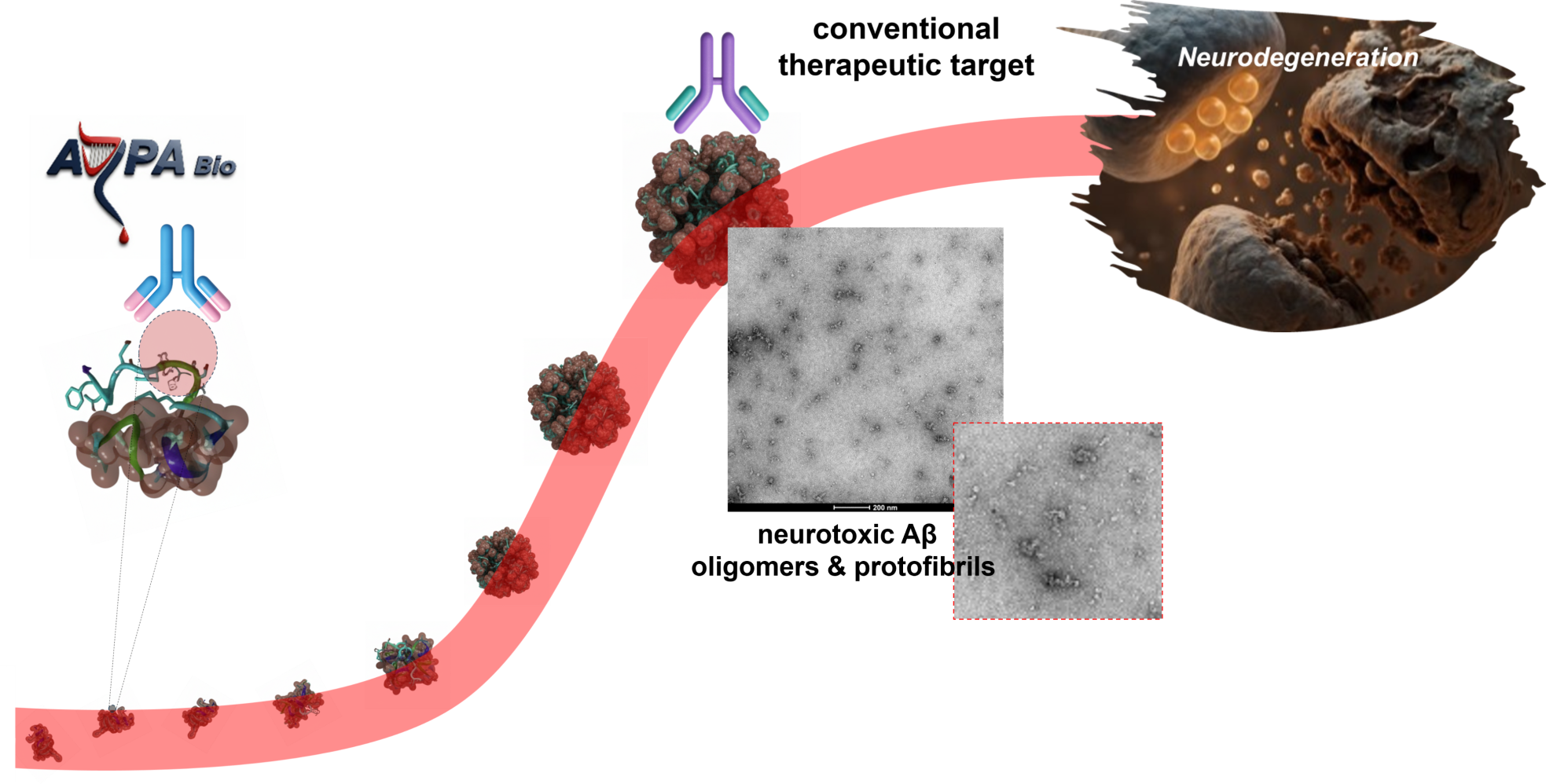
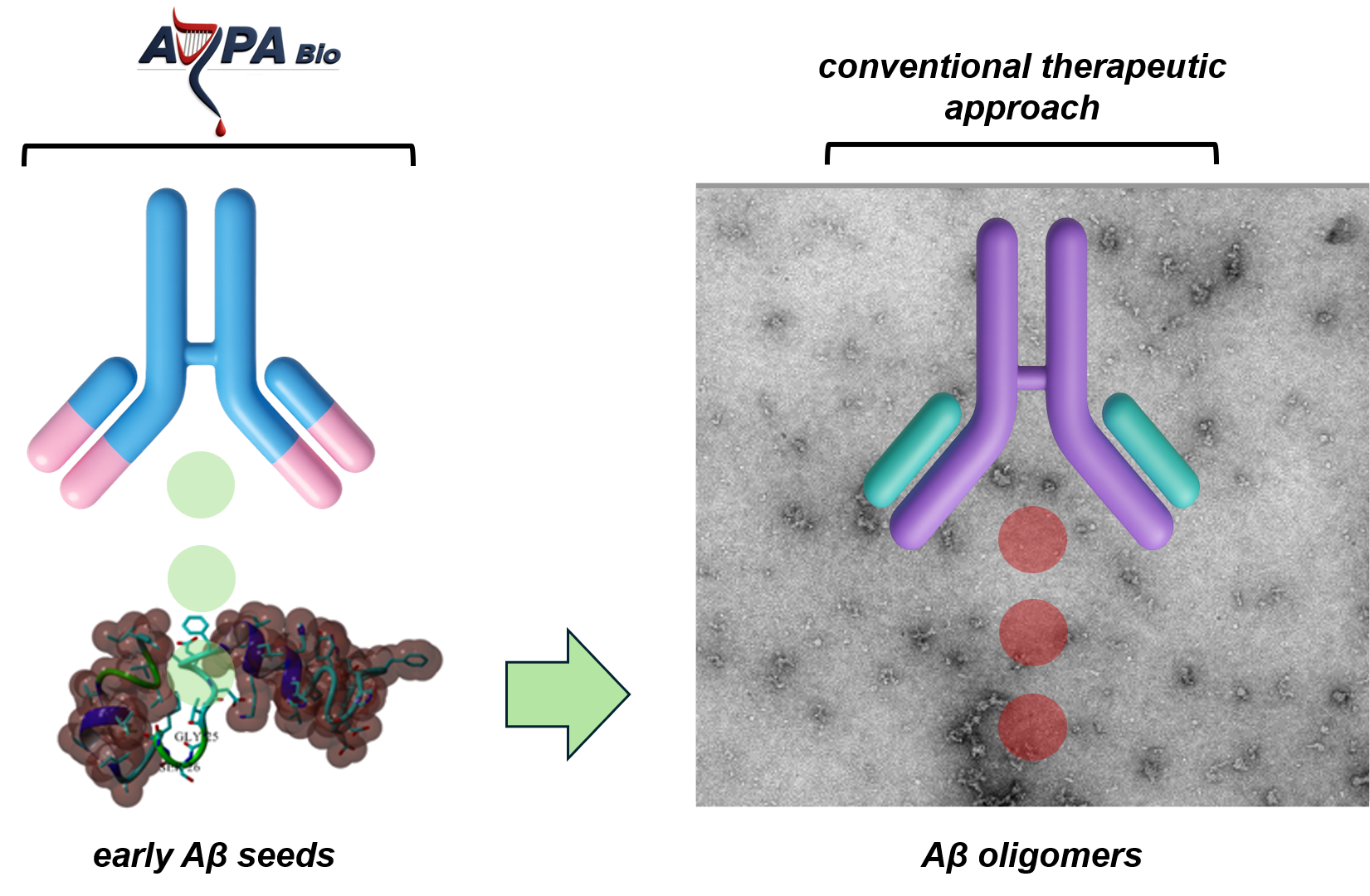
ARPA Bio's therapeutic approach involves targeting key molecular events associated with the early, pathological protein misfolding, which eventually leads to the formation of large, neurotoxic protein aggregates referred to amyloid-beta oligomers (image above). ARPA Bio has identified several, proprietary targets (epitopes) associated with this early stage of pathological protein misfolding, which offers novel therpeutic advantages and therefore distinguishes from the currentlty available (FDA approved) immuno-therapies.
How does ARPA Bio's therapeutic and diagnostic strategy differentiate from earlier, clinically approved antibodies ?
ARPA Bio targets early, molecular seeds of pathological protein species (left) during the long, insiduous phase of the disease (estimated 10-20 years before clinical manifestation). This unique strategy enables, for the first time, a highly selective targeting of the root cause of the disease and prior to the accumulation of neurotoxic oligomers. Oligomers are neurotoxic protein aggregates (e.g, right: electron microscopy imaging of oligomers) consisting of a meta-stable and heterogenous morphology. The detection of these pathological species may already be associated with advanced disease progression, which is why it is important to therapeutically slow or block the formation of these oligomers species before they bind to neurons and induce neurodegeneration. The currently available and FDA approved immuno-therapies for AD aim at targeting mature oligomers (right). Therefore, ARPA's unprecedented therapeutic strategy focuses on rather fighting the disease at a much earlier time point, by targeting specific, early molecular events occuring during the early phase of the disease.
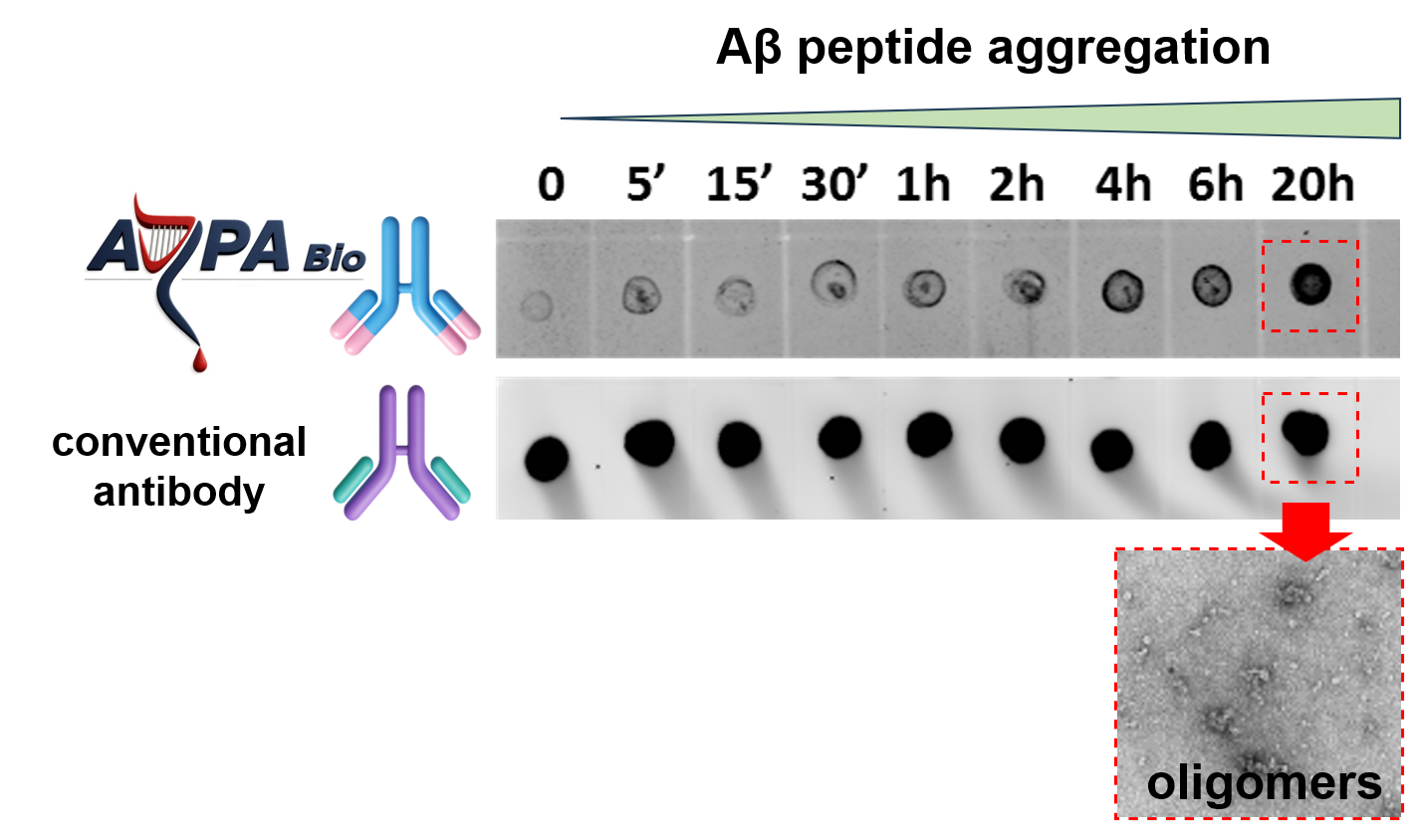
ARPA's antibody molecules do not bind non-toxic monomers but rather highly specific seeds that gradually appear during the time course of amyloid-beta aggregation leading to the accumulation of neurotoxic oligomers, as shown by the dotblot screening. Conventional anti-amyloid beta antibodies, (6E10 or 4G8), do not distinguish between soluble monomers (t= 0) and neurotoxic oligomers (t=4-20hrs), wherease ARPA's antibodies only bind to highly specific (proprietatry) epitopes, that emerge during the early aggregation process. ARPA's unique strategy enables targeting several, different (proprietary) epitopes, which have been shown to be highly relevant during the early, pathological process of amyloid-beta misfolding.
